what is pulse?
Pulse is defined as a pressure distension wave produced by the contraction of the left ventricle against a partially filled aorta which is transmitted to peripheries and is felt on a peripheral artery against a bony prominence.
How to assess pulse?
| Rate | In radial artery |
| Rhythm | In radial artery |
| volume | carotid artery |
| character | Carotid artery (Remember we check collapsing pulse, pulsus alternans and pulsus paradoxus in radial artery) |
| radio-radial and radio-femoral delay | |
| weather all peripheral pulses are felt | |
| condition of vessel wall | stiff in Elderly |
How to take your pulse ?
RATE -In radial artery
Using 3 fingers felt lateral to flexor carpi radialis tendon in semipronated and wrist slighlty flexed for 15 seconds and multiply by 4
Why use 3 fingers to take pulse ?
The distal finger to prevent backflow, proximal finger to stbilize artery on the bone and middle finger is used to feel
What are the Causes of decreased pulse rate?
Bradycardia is defined when pulse rate is less then 60
- Physiological -sleep athletes
- pathological – (remember hypo condition)
- like hypoxia, hypothermia and
- hypothyroidism(myxedema)
- drugs like beta-blockers verapamil digoxin sick
- sinus syndome
- cushing’s reflex ( decreased respiration ,bradycardia and convulsions when intracranial tension is raised)
What are the causes of increased pulse pressure?
Tachycardia is defined when pulse rate is more then 100
- physiological- exertions, anxiety, pregnancy, emotion, exertion
- High output states-Severeanemia, thyrotoxicosis, beriberi, Paget’s disease cirrhosis of liver, AV fistula
- Drugs (e.g.atropine, nifedipine, salbutamol, terbutaline, nicotine, and caffeine intake
What is the Relationship between pulse and temperature?
For every 1F rise in temperature , pulse is increased by 10
What are the causes of Relative bradycardia?
- (Mostly viral condition)
- dengue, brucellosis ,typhus ,leptospirosis
- legionella, psittacosis, meningitis
- non-infectious ( beta-blockers, lymphomas, factitious fever, drug fever)
What are the causes of Relative Tachycardia?
- Acute rheumatic carditis,
- Diphtheric myocarditis
- Tuberculosis
RHYTHM
Measured In radial artery
What are the various irregular RHYTHM?
| Regularly irregular – atrial tachyarrhythmias with fixed AV blocks, sinus arrthmia |
| Irregularly irregular – Atrial fibrillation, Atrial tachyarrhythmias with varying AV blocks |
| Regular with occasional irregularity- extrasystoles |
Is there any Arrthmias with regular rhythm?
Yes , like in atrial flutter , ventricular tachycardia, first degree heart block, second degree heart block
What is pulse deficit?
Difference between heart rate (counted by steth ) and pulse rate when counted simultaneoulsy for one full minute by 2 individual
Can pulse deficit be measured by 1 individual?
Yes, but there is more error because pulse is irregular . Done separately for 1 minute
What if deficit is more then 10?
| atrial fibrillation | Ventricular premature complexes | |
| apex pulse deficit | usually >10 | usually <10 |
| JVP a wave | absent | present |
| s1 | variable intensity | normal |
What is the volume of pulse?
Its the measure of the pulse pressure
What are causes of hypokinetic pulse?
- Congestive cardiac failure
- Hypovolemia
- Shock
- MS
- AS
- Constrictive pericarditis
what are the causes of Hyperkinetic pulse?
- Physiological like fever ,pregnancy, alcoholism and exercise
- Pathological like high output states (already mentioned), AR , PDA ,severe MR
what are the causes of varying volume ?
-atrial fibrillation
KNOW about CHARACTER
Checked in carotids with thumb , one side at one time near the upper neck between the sternomastoid and trachea at the level of cricoid cartilage and repeat the procedure on the other side
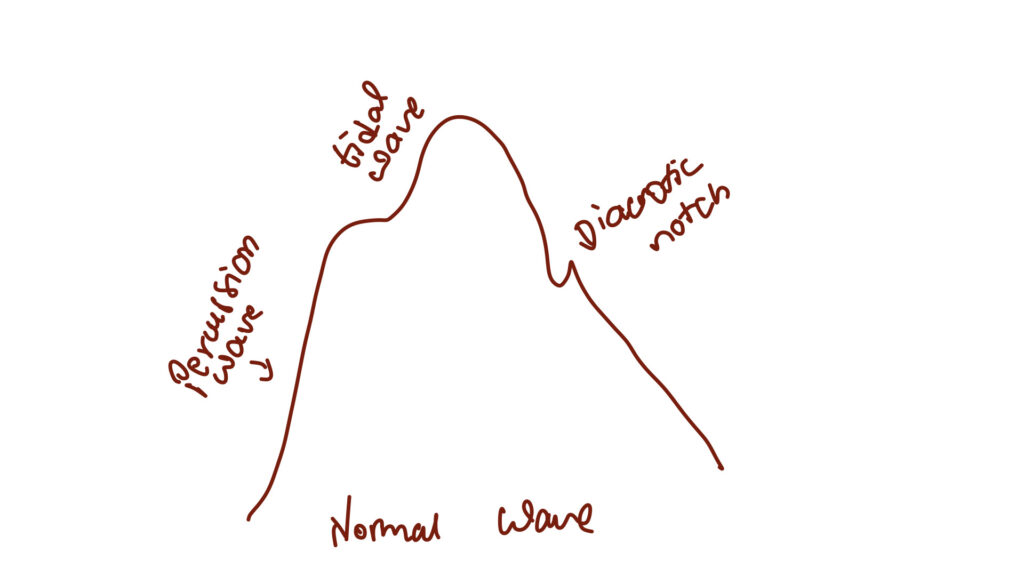
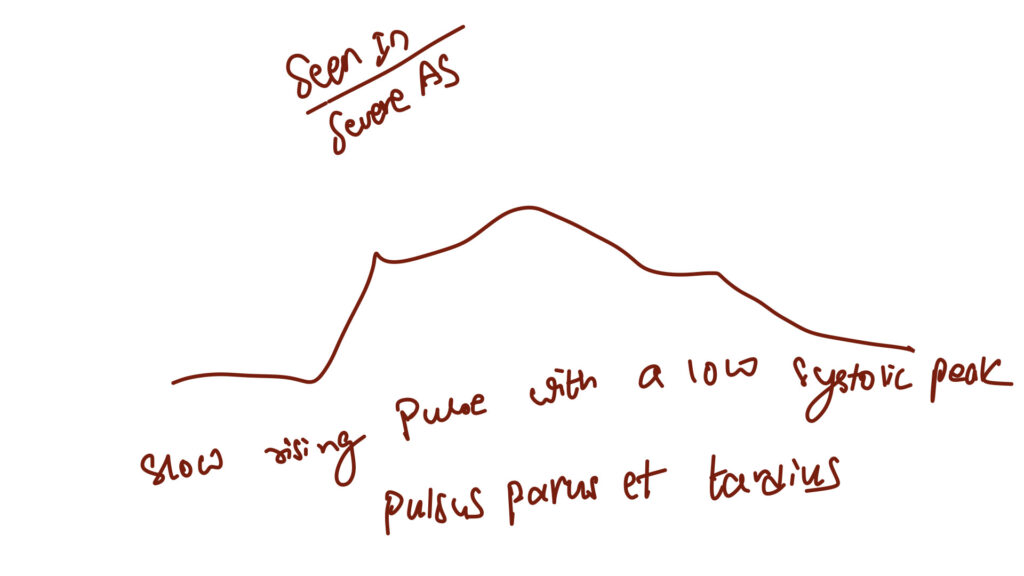
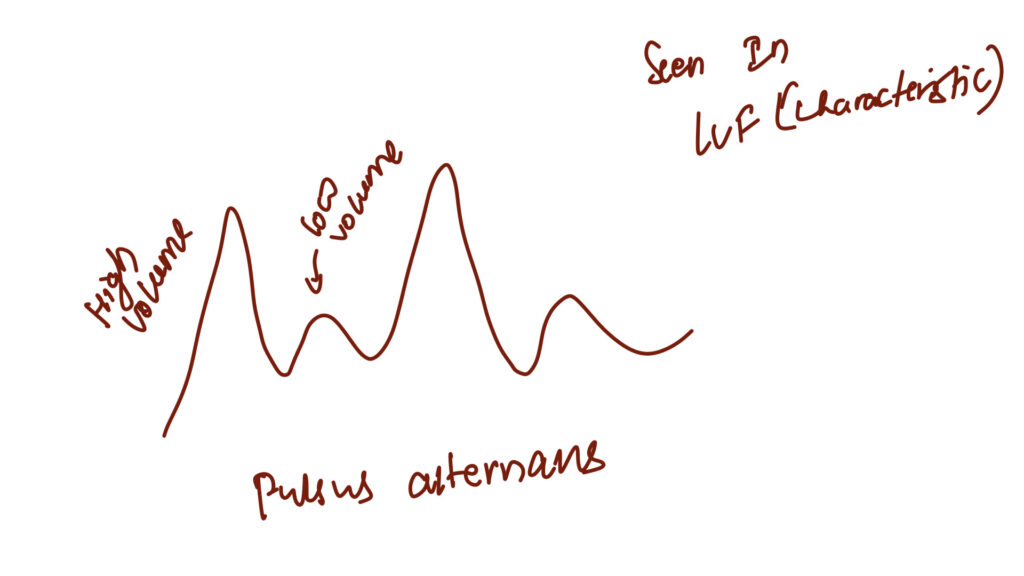
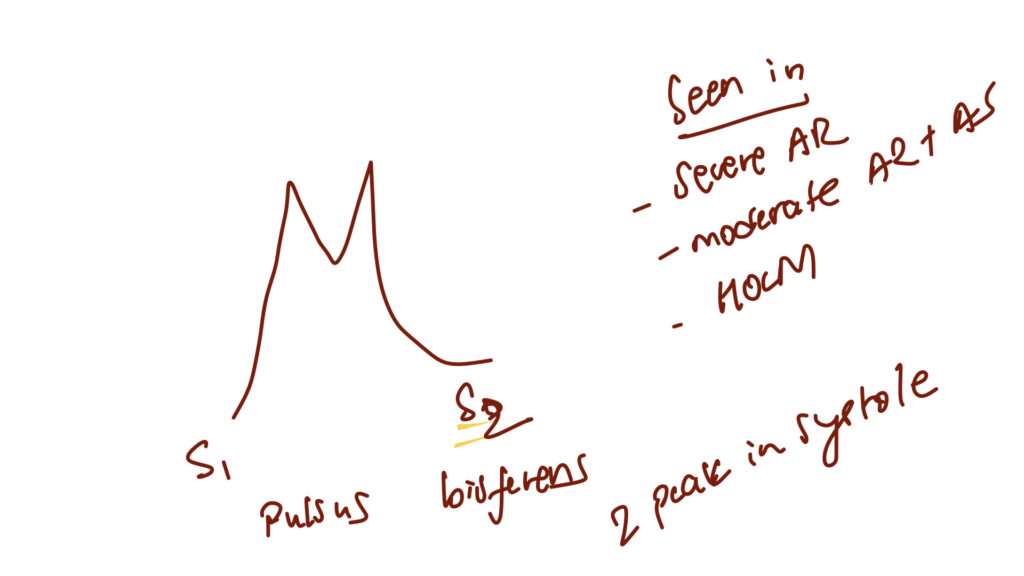
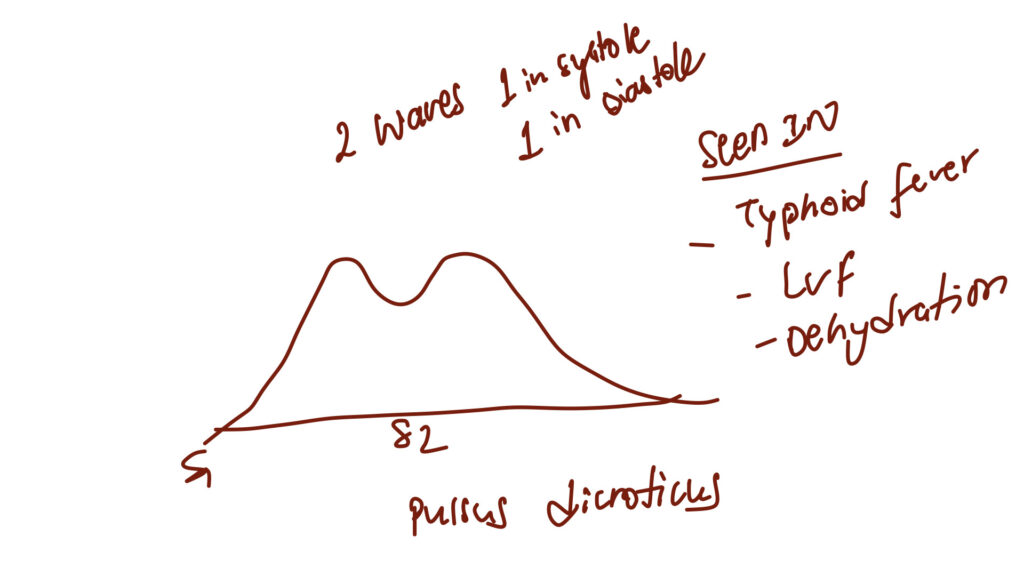
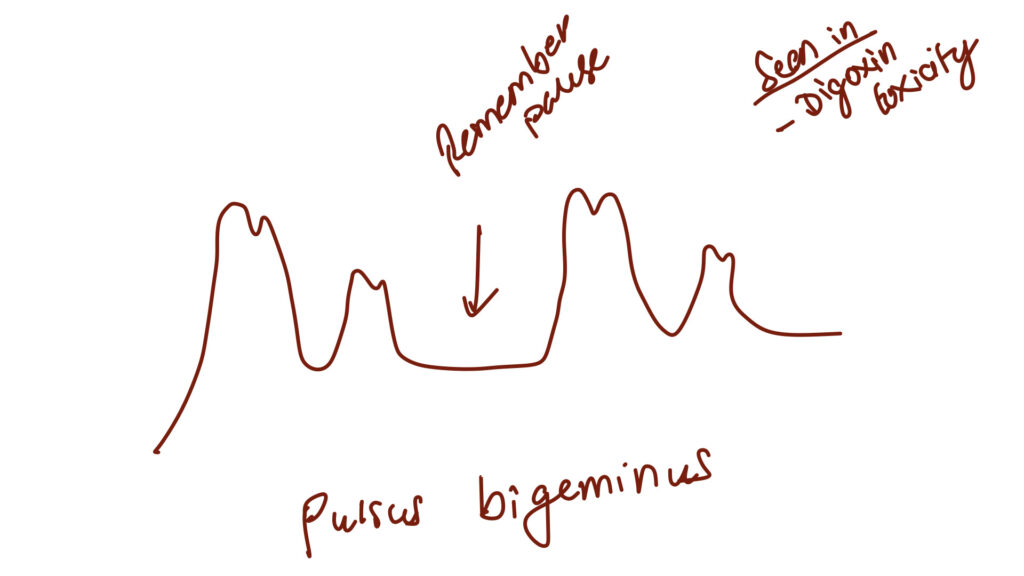
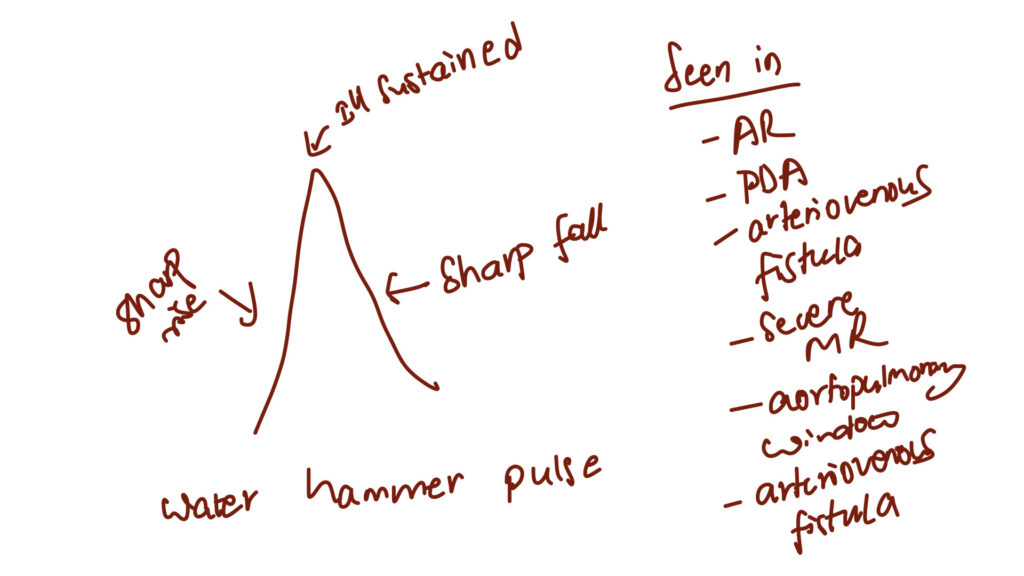
Normal pulse character – catacrotic pulse
What is pulsus paradoxus ?
Systolic blood pressure falls more than 10 mm Hg during inspiration (exaggeration of normal phenomenon) seen in
- Constrictive pericarditis
- Acute severe asthma/ COPD
- Cardiac temponade , tension pneumothorax and massive pulmonary embolism
- Anaphylatic shock and obesity
How to take collapsing pulse?
Palpate the radial artery , wrap your wrist around the patient’s forearm ,so as to place the heads of the metacarpals over the artery, now abruptly raise the patients arms above the shoulder joint.
How to palpate brachial pulse ?
Examiners support the patient’s forearm in this left hand and patient’s upper arm abducted , the elbow slightly flexed and the forearm externally rotated , the examiner’s right hand is then curled over the anterior aspect of the elbow to palpate along to course of the artery just medial to the biceps tendon and lateral to the medical epicondyle of the humerus . The position of the hands should be switched when examining the opposite limb.
How to take femoral pulse?
Best palpated into the upper thigh from beneath the inguinal ligament one-third of the distance from the pubis to the anterior superior iliac spine.
How to take popliteal artery pulse?
The pulse is detected by pressing deeply into the popliteal space with the supporting fingertips. Felt most conveniently with the patient in the supine position and examiner’s hands encircling and supporting the knee from each side .(patient should be instructed to go limp)
How to take posterior Tibial artery?
Felt just posterior to the medial malleolus between the medial malleolus and the Achilles tendon , above the calcaneus.
How to take Dorsalis pedis artery?
recumbent position and the ankle is relaxed . Artery is palpated lateral to extensor hallucis tendon , against the navicular bone.
What are causes of the Radio-radial delay?
- Coarctation of the aorta (subclavian)
- Thoracic outlet syndrome
- Aortic arch aneurysm
- Takayasu’s dsease
What is the cause of Radio-femoral delay?
- Coarctation of the aorta
